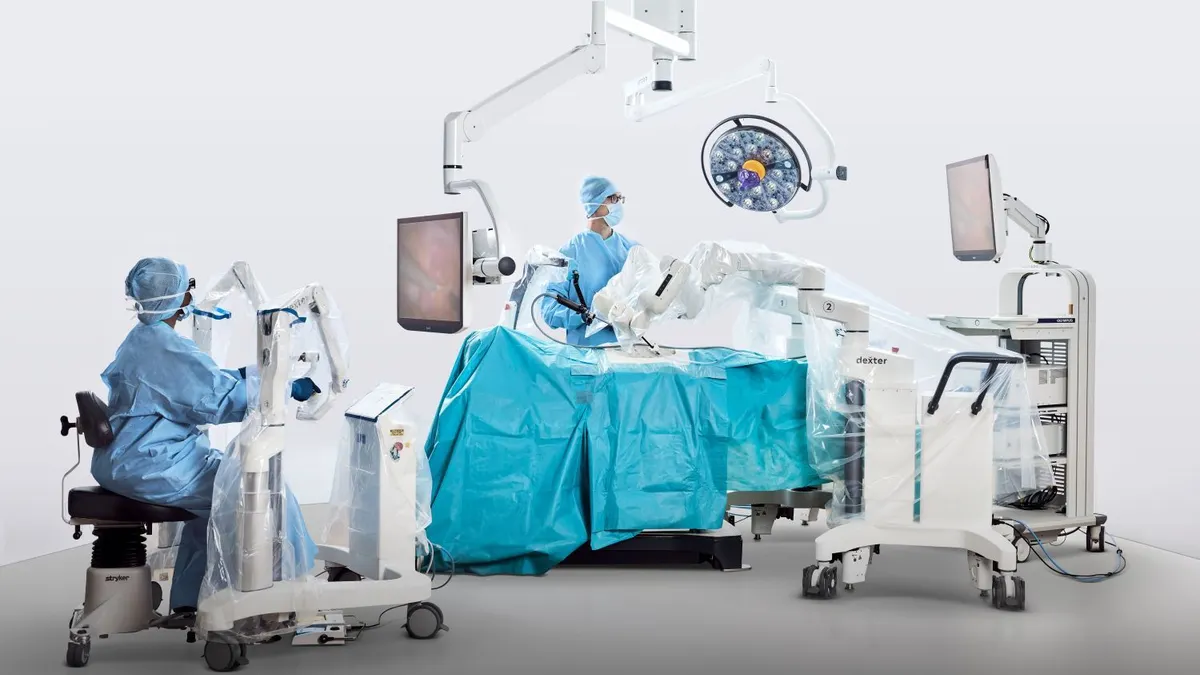
Distalmotion said this week that its Dexter robot received the Food and Drug Administration’s 510(k) clearance for hysterectomy procedures, as the company expands its focus on high-volume soft tissue surgeries and outpatient sites.
It is the Switzerland-based company’s third authorization in the U.S., following gallbladder removal in May and inguinal hernia repair last October. Distalmotion is also studying the robot’s use in ventral hernia repair and uterine fibroid removal and recently completed a clinical trial for pelvic organ prolapse.
The latest clearance covers ovary and fallopian tube removal and other gynecologic procedures, in addition to total benign hysterectomy. The authorization includes system enhancements to improve operating room setup, procedural workflow and instrument performance.
Hysterectomy, one of the highest-volume gynecologic surgeries, is increasingly performed in outpatient settings, the company said.
Distalmotion, which is targeting hospital outpatient and ambulatory surgery centers with a robot that is small and mobile, is among the companies giving Intuitive Surgical competition in soft tissue robotic procedures.
In June, Distalmotion announced its first multi-robot sale in the U.S. to AdventHealth, which operates 50 hospitals in nine states.
Erica Stockwell, a gynecology surgeon at AdventHealth Celebration in Florida, said access to robotics has been a challenge for gynecologists due to limited scheduling availability. “DEXTER solves this with a mobile robot that can be shared by various specialties,” Stockwell said in Distalmotion’s statement. The robot allows immediate bedside access to the patient, she added, helping to reduce staffing needs.
The Dexter robot has been used in over 2,000 procedures, spanning more than 30 procedure types in general, gynecological, colorectal and urological surgery.
AiM Medical raises $8.1M
AiM Medical Robotics said Tuesday it closed an $8.1 million Series A financing round, including $3.8 million in notes converted into equity, to support its neurosurgery platform that allows surgeons to perform procedures within an MRI.
The system combines intraoperative MRI and robotic guidance to place neurostimulation leads for Parkinson’s disease patients. The robotic surgery platform is designed for a range of cranial procedures, including biopsy, tumor ablation, epilepsy ablation and targeted intracranial drug delivery.
The technology, which is preparing for first-in-human trials, eliminates the need to move patients between operating rooms and imaging suites, the Worcester, Massachusetts-based company said.
IQ Capital and 1540 Ventures led the funding round. Additional participants included Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Sontag Innovation Fund, Cancer Research Horizons, and Harvard Business School Alumni Angels.
AiM has raised more than $11.3 million in total, in addition to federal grant support for the technology.